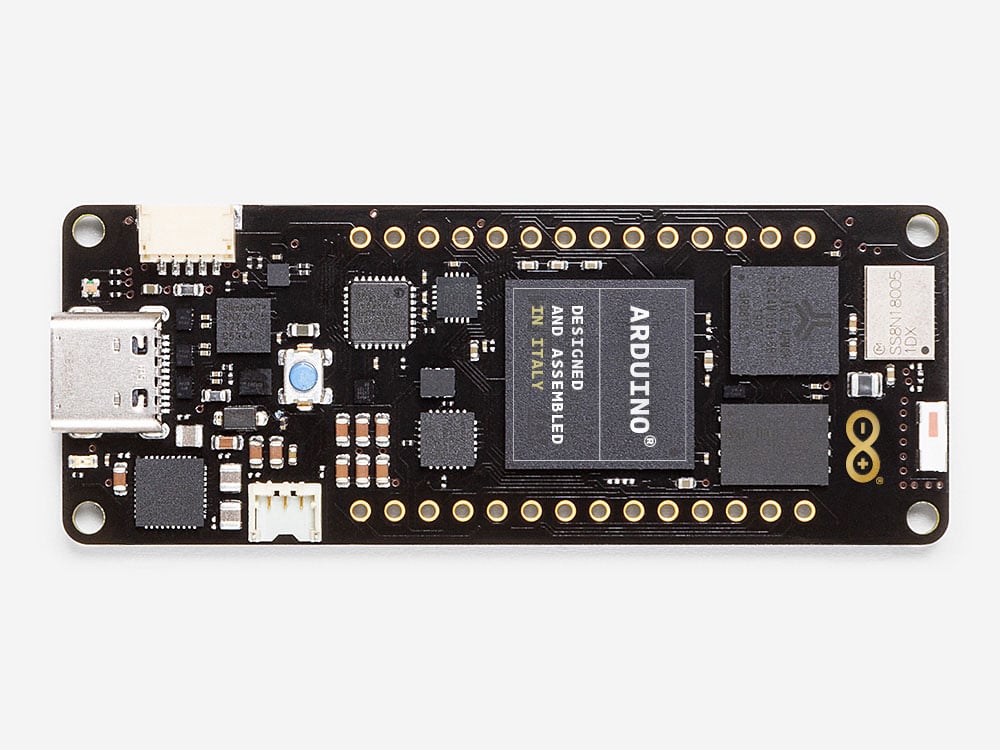
But that’s not all. At CES 2020, we are also excited to announce the powerful new Arduino Portenta family. Designed for demanding industrial applications, AI edge processing, and robotics, it features a new standard for open high-density interconnect to support advanced peripherals. The first member of the family is the Arduino Portenta H7 module – a dual-core Arm Cortex-M7 and Cortex-M4 operating at 480MHz and 240MHz, respectively, with industrial temperature range (-40 to 85°C) components. The Portenta H7 is capable of running Arduino code, Python and JavaScript, making it accessible to an even broader audience of developers.
The new Arduino Portenta H7 is now available for pre-order on the Arduino online store, with an estimated delivery date of late February 2020.
Portenta H7 simultaneously runs high-level code along with real-time tasks. The design includes two processors that can run tasks in parallel. For example, is possible to execute Arduino compiled code along with MicroPython one, and have both cores to communicate with one another. The Portenta functionality is two-fold, it can either be running like any other embedded microcontroller board or as the main processor of an embedded computer. Use the Portenta Carrier board to transform your H7 into an eNUC computer and expose all of the H7 physical interfaces.
Portenta can easily run processes created with TensorFlow™ Lite, you could have one of the cores computing a computer vision algorithm on the fly, while the other could be making low-level operations like controlling a motor, or acting as a user interface.
Use Portenta when performance is key, among other cases, we envision it to be part of:
- High-end industrial machinery
- Laboratory equipment
- Computer vision
- PLCs
- Industry-ready user interfaces
- Robotics controller
- Mission-critical devices
- Dedicated stationary computer
- High-speed booting computation (ms)
Two Parallel Cores
H7’s main processor is a dual-core unit made of a Cortex® M7 running at 480 MHz and a Cortex® M4 running at 240 MHz. The two cores communicate via a Remote Procedure Call mechanism that allows calling functions on the other processor seamlessly. Both processors share all the in-chip peripherals and can run:
- Arduino sketches on top of the Arm® Mbed™ OS
- Native Mbed™ applications
- MicroPython / JavaScript via an interpreter
- TensorFlow™ Lite
Graphics Accelerator
Probably one of the most exciting features of the Portenta H7 is the possibility of connecting an external monitor to build your own dedicated embedded computer with a user interface. This is possible thanks to the processor’s on-chip GPU, the Chrom-ART Accelerator™. Besides the GPU, the chip includes a dedicated JPEG encoder and a decoder.
A new standard for pinouts
The Portenta family adds two 80 pin high-density connectors at the bottom of the board. This ensures scalability for a wide range of applications by simply upgrading your Portenta board to the one suiting your needs.
On-board Connectivity
The onboard wireless module allows to simultaneously manage WiFi and Bluetooth® connectivity. The WiFi interface can be operated as an Access Point, as a Station or as a dual-mode simultaneous AP/STA and can handle up to 65 Mbps transfer rate. Bluetooth® interface supports Bluetooth Classic and BLE. It is also possible to expose a series of different wired interfaces like UART, SPI, Ethernet, or I2C, both through some of the MKR styled connectors, or through the new Arduino industrial 80 pin connector pair.
USB-C Multipurpose Connector
The board’s programming connector is a USB-C port that can also be used to power the board, as a USB Hub, to connect a DisplayPort monitor, or to deliver power to OTG connected devices.
Multiple options in one board
Order the default Arduino Portenta H7 (codename H7-15EUNWAD) that comes with:
- 2MB SDRAM
- 16MB NOR Flash
- 10/100 Ethernet Phy
- USB HS
- NXP SE050C2 Crypto
- WiFi/BT Module
- Ceramic Antenna
- DisplayPort over USB-C
If you need more memory, Portenta H7 can host up to 64 MByte of SDRAM, and 128 MByte of QSPI Flash. Order it with an external UFL connector for adding a higher-gain antenna to the board. Decide between crypo-chips from Microchip® and NXP. The board is highly customizable in volumes, ask our sales representatives for options.
Pinout Diagram
The Portenta H7 follows the Arduino MKR form factor but enhanced with the Portenta family 80 pin high-density connector. Learn more about the board’s pinout by reading the board’s pinout documentation.
Download the full pinout diagram as PDF here.
Source Arduino.cc

